 |
| Image Credit: Google |
Analysis
The US-Mexico border stretches for nearly 2,000 miles,
winding its way from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico. This international boundary separates not
just two countries, but also two vast cultural landscapes. Understanding the US-Mexico border requires a
deep dive into its history, its economic significance, and the ongoing social
and political complexities that surround it.
A Storied History: From Treaties to Tensions
The US-Mexico border has been shaped by numerous treaties and
agreements over the course of centuries.
The Adams-Onís Treaty of 1819 established the initial border after
Mexico gained independence from Spain.
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, following the Mexican-American
War, ceded a significant portion of Mexican territory to the United States,
solidifying much of the current border's path.
The Gadsden Purchase of 1854 further refined the border, with
the US acquiring additional land. These
historical agreements laid the groundwork for the complex relationship that exists
today.
A Hub of Commerce: Trade and Economic Ties
The US-Mexico border is not just a line of division, but also
a vital economic artery. It is the
busiest international border in the world, facilitating billions of dollars in
trade every year. Goods from
manufacturing plants and agricultural fields on both sides flow freely,
creating a deeply integrated economic zone.
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), implemented
in 1994, further boosted cross-border trade and investment. The US-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), its
successor, aims to maintain this economic partnership while addressing some of
NAFTA's shortcomings.
A Humanitarian Challenge: Migration and Security
The US-Mexico border is also a focal point for
migration. People from Mexico, Central
America, and other countries seek to enter the US for various reasons,
including economic opportunity, reuniting with families, and fleeing
violence. This influx of migrants
presents both humanitarian challenges and security concerns.
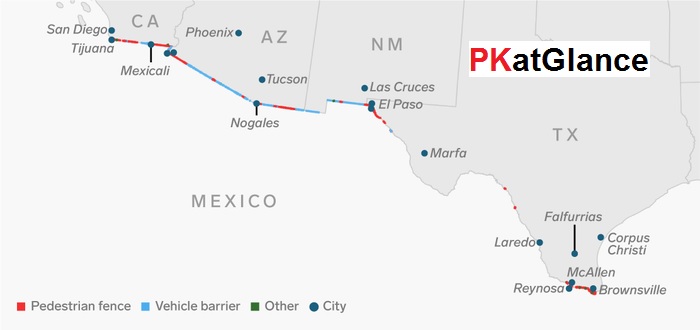
The US government has implemented various border security
measures, including physical barriers, increased border patrol presence, and
stricter immigration policies. However,
debates persist about how best to manage migration flows while balancing
humanitarian concerns with national security.
Looking Ahead: A Border in Flux
The US-Mexico border is a dynamic place, constantly evolving
in response to economic, political, and social forces. Finding common ground on how to manage
migration, strengthen economic ties, and ensure security cooperation will be
crucial for navigating the complexities of this ever-changing border landscape.

Post a Comment